
How Powerful is the Sun?
Ah, the Sun. We stay warm under it, tan under it and it gives life to every living thing on this planet. But it is 93,000,000 miles away. That is so far that if you were flying to the sun at 550 MPH, it would take you 17 years to get there. If the Space Shuttle, traveling at 27,000 MPH would go there, it would reach the sun in about 156 days.
Let’s Talk Distance First
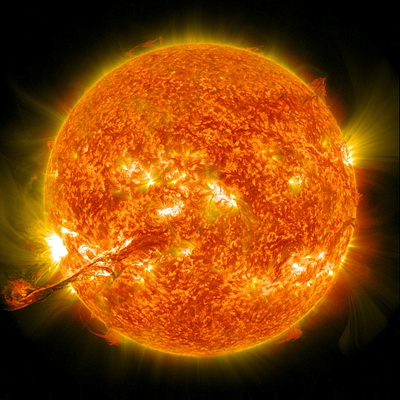
When you look at the sun, you are actually seeing the way it looked about nine minutes ago. In the photo above, we see a large solar flare extending out from the Sun’s surface, but if you looked at the sun right now, you wouldn’t see the flare. You would have to wait another nine minutes before it would appear.
A more dramatic scenario is that if the Sun blew up right now, we wouldn’t know about it until about nine minutes later, but no worries, the sun won’t leave us for another four or five billion years, so you have time to prepare. These examples boil down to the fact that it takes the light from the Sun that long to reach us.
Don’t Underestimate Its Power
Even at that distance, don’t let your curiosity get the best of you by starring at the sun, or you will go blind! And don’t get silly and stay on the beach without proper lotion or you will be visiting the dermatologist shortly after that.
We are not saying this to scare you, well, maybe in part, but our main purpose is to give you an idea just how powerful this star, and it is a medium sized star by the way, it really is.
The bottom line is that an object that is 93 million miles away and can still cause this serious damage to every living organism on this planet gives you a good idea of how powerful this gas giant is.
How Big is the Sun When Compared to Other Stars?
We previously mentioned that our Sun is a medium sized star. For a comparison of the size of our Sun relative to other stars in our galaxy, take a look at this video and get ready for a mind-boggle!
Brief Overview of the Sun’s Lifecycle
In about five billion years, this star will have lost all its hydrogen fuel, which is the element that allows the fusion process to proceed. The result is that it will turn into what astronomers call a red giant.
When a star starts turning into a red giant, it begins to expand to an enormous size. So big that its size could engulf virtually all the inner planets in it our solar system. For our solar system, that includes Mercury, Venus, and you got it – Earth.
As mentioned, we won’t see the Sun’s demise for another 4.5 billion years, so when it begins its red giant cycle, you might want to pack some beers and enjoy watching this event while relaxing on your porch and having a beer or two before you say goodbye!
Energy
The energy of this sun is mind-boggling. It produces energy that is the equivalent of one-trillion megaton bombs per second. Yes, you heard right. That’s 67,000 times as powerful as the bomb that was dropped on Hiroshima and this occurs every second!
So what is it about this medium-sized star that can be the difference between life and death on Earth? Why is it so powerful? What is it made of?
Let’s Start with Fusion
Fusion is the process of atoms merging into another atom. In the case of our Sun (and most other stars) four hydrogen atoms fuse into one helium atom, which is the result of extreme heat that causes gravity to allow this phenomenon to occur.
Not all the mass of the four hydrogen atoms is converted into one helium atom, as the total amount of the mass of the four hydrogen atoms does not equal the total mass of the assimilated helium atom, so something must give. And what gives is energy. A lot of it. About four million times more energy than the burning of coal.
More precisely, only 71% of the total mass of the four atoms is fused with the hydrogen atom. This is the foundation of Einstein’s formula E=MC2. The more mass that is released, the more energy that is created. So for fusion reactions to occur, Briticana.com sums it up quite clearly: “The total mass of the resultant particles is less than the mass of the initial reactants”. Basically, it is saying that mass and energy are different forms of the same thing, so if the mass of an object gives, the result is energy.
As we mentioned, these fusion reactions occur every second. No wonder we can go blind if we look at the Sun.
More about how this entire fusion process works can be found here.
The Sun’s Structure
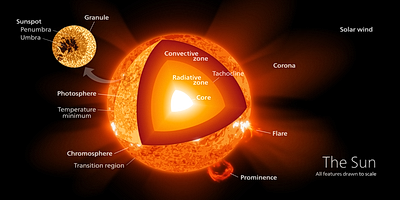
Imagine a ball of gas that is 865,370 miles in diameter. That’s our Sun. There are no solid materials in this star (or in any star in the universe). Just hot gasses, very hot. 9,900 degrees Fahrenheit hot!
With that said, the Sun is divided into four layers: the photosphere, chromosphere, corona, and heliosphere. Let’s take a look.
-
-
- Core – The core is where the fusion process occurs. As the hydrogen atoms merge into the helium atoms, energy in the form of light is generated.
- Radiative Zone – This zone radiates (transfers light and heat).
- Tachocline – The atoms are radiated through this thin boundary region and then move to the convective zones.
- Convective Zone – Convection is the process by which less dense material rises. This part of the Sun is much cooler than its inner layers, but the result of this process is where we see the light and feel the heat of the Sun.
-
There are much brighter stars than the Sun. Some are called “supergiants” or “hypergiants.” These giants can be over 100 times more luminous than our own ball of gas! Now, just imagine how powerful their fusion reactions are!
Types of Stars
There are many different types of stars in our galaxy. The types of stars are classified by the following criteria:
-
- Temperature – Hot stars are blue or white, while cooler stars are orange or red
- Mass – Massive stars burn out quickly, while less massive ones can last millions of years
- Spectral Type – Stars can be identified through their colors and temperatures
Conclusion
The Sun is nothing but a huge hot ball of gas, but show some respect, because this great gas ball is what keeps us alive. Amazingly, it supplies life to this planet even though it is 93,000,000 miles away.
The center of the Sun is the core, where the temperatures are millions of degrees. The core’s pressure from gravity causes hydrogen to fuse together to form helium, which is the fusion process.
The Sun doesn’t have an electrical charge, so it doesn’t produce light on its own. The heat of the core makes the gas around it become extremely hot, and this is what makes it glow.
Our Sun is a type of star called a yellow dwarf. There are other different types of stars that are of different sizes and temperatures.
So there are many different stars in the universe and our Sun is one of them. They are all so powerful that staring at them for more than a second can make you blind. So accept the fact that this star is powerful, but don’t look up to find out!
