Cars and trucks consist of a vast number of mechanical, electrical, and electronic components, all working in tandem to ensure that the vehicle moves smoothly and safely.
In this article, we will explore the various parts that make up a car and how they work together to power the vehicle.
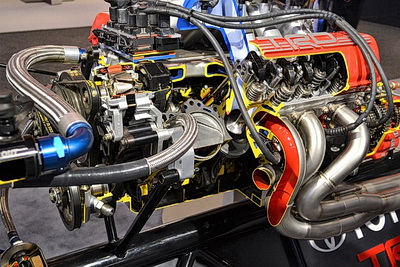
Engine
Aside from electronic vehicles (EVs) which don’t use gas engines, all other vehicles are gas or diesel-powered. In this article, we will focus on the conventional gas engine that is in the majority of vehicles used in the United States and across most parts of the world at this time.
The engine is the heart of the car, and it is responsible for converting fuel into mechanical energy, meaning that the fuel is ignited and causes a piston to move up, pushing a bar (camshaft) to rotate. The camshaft is connected to the vehicle’s wheels and subsequently, causes the wheels to move.
There are usually six or eight pistons in the engine that are ignited simultaneously and moves the camshaft. The more pistons in the engine, the more power is applied to the camshaft and the faster the car can go.
A fuel injector sprays a precise amount of fuel into each cylinder, which mixes with air and ignites when the spark plug generates a spark.
Powertrain
Transmission

The transmission is responsible for transmitting the power generated by the engine to the wheels. It contains more parts than the entire car, and of these parts, it is the gears that are the most important component.
The gear ratios, which refer to the size proportions between one gear and another are what allow the vehicle to move at different speeds. The driver can select different gears using the gear selector or shift paddles, which changes the gear ratio and alters the car’s speed.
Besides choosing your desired speed, the transmission contains the standard PRD (Park, Reverse, and Drive) gears that we are all accustomed to.
Drivetrain

This component is another component of the car’s powertrain. It connects the transmission to the wheels and consists of several individual parts, such as the driveshaft, differential, and axles.
The driveshaft transfers the power from the transmission to the differential, which splits the power between the two wheels. The axles then transfer the power from the differential to the wheels, which allows the car to move forward.
Breaks

The brakes consist of a series of discs or drums that slow down the wheels when the driver presses the brake pedal.
When the brake pedal is pressed, brake fluid is forced into the brake caliper or wheel cylinder, which presses the brake pads or shoes against the brake discs, creating friction that slows down the wheels.
Suspension
The suspension system is responsible for keeping the car’s wheels in contact with the road and providing a smooth ride. It consists of several components such as the shocks, struts, springs, and control arms. The shocks and struts absorb the impact of bumps and potholes, while the springs support the weight of the car and allow it to absorb energy from uneven surfaces. The control arms connect the suspension to the chassis and allow for smooth movement of the wheels.
Steering
The steering system is responsible for controlling the direction of the car. It consists of several components such as the steering wheel, steering column, and steering rack. When the driver turns the steering wheel, it turns the steering column, which rotates the steering rack. The steering rack is connected to the front wheels and turns them in the desired direction.
The electrical system is responsible for providing power to the car’s various electronic components such as the lights, radio, and navigation system. It consists of several components such as the battery, alternator, and wiring harness. The battery provides the initial power to start the car and provides power to the car’s various systems when the engine is not running. The alternator generates electricity when the engine is running and charges the battery.
Finally, the body of the car is responsible for protecting the passengers and providing a comfortable environment. It consists of several components such as the frame, body panels, and interior. The frame provides structural support for the car and protects the passengers in the event of a collision. The body panels provide aerodynamic properties and protect the car from weather and other external elements. The interior provides a comfortable environment for the passengers and includes seats, air conditioning, and entertainment systems.
Conclusion
Automotive vehicles are complex machines consisting of various mechanical, electrical, and electronic components that work in tandem to provide power, safety, and comfort. Understanding the various parts that make up a car is essential for proper maintenance and troubleshooting.
